HCX Use cases:
- Workload migration from legacy infrastructure to modern Software Defined Data Center, for example a new software defined data center as a destination powered by VMware Cloud Foundation with the latest software releases.
- Workload migration from non-vSphere infrastructure as a source to latest VMware infrastructure as a destination/target. This is useful for customers moving to VMware infrastructure.
- Workload rebalancing: Where you not only move the workload from on-premises data center to the cloud but you also have the ability to move the workload back to your on-premises data center.
- Network layer 2 extension: Allow layer 2 network extension between:
- Private VMware SDDC to another Private VMware SDDC
- Private VMware SDDC to Public Cloud such as AWS, Google, Azure, Oracle cloud.
- Public cloud (AWS, Google, Azure, Oracle) to another public cloud
With network extension, workload can move to another site without the need to re-IP the workload, workload can continue to retain the original IP address. Also the workload is able to establish layer 2 adjacency with other existing workloads in the original site which are in the same subnet even though the workload has moved to another data center/site.
- Zero downtime migration of workloads between different data centers/sites.
- WAN Optimization: This is achieved by using specific HCX appliance which optimizes traffic utilization over costly WAN links using techniques such as de-duplication and line conditioning.
- Disaster recovery: Using this capability, HCX can protect and replicate virtual machines in remote data center.
HCX Architectural Components:
Management Component:
HCX Manager: This is the first component that gets deployed before the data plane components (HCX service mesh) are deployed. HCX Manager should be treated similar to other management components such as vCenter Server, NSX Manager and as such should connect to VM Management network. HCX Manager typically resides on a management cluster which is dedicated for management components.

HCX Manager comes in two flavors:
a. HCX connector at source and using which one can establish unidirectional site pairing towards target HCX cloud manager in target site. HCX Connector is always deployed as the source. An HCX Connector cannot be paired with another HCX Connector.
b. HCX Cloud Manager which provides bidirectional site pairing between HCX managers deployed across sites.
We need to understand the difference between unidirectional site pairing and bidirectional site pairing.
Unidirectional site pairing:
HCX Connector creates a unidirectional site pairing to an HCX Cloud system.
In this type of site pairing, all HCX Service Mesh (data plane of VMware HCX) connections, Migration and Network Extension operations, including reverse migrations, are always initiated from HCX Connector.
Above figure shows unidirectional site pairing between HCX connector at source with HCX Cloud Manager at target site.
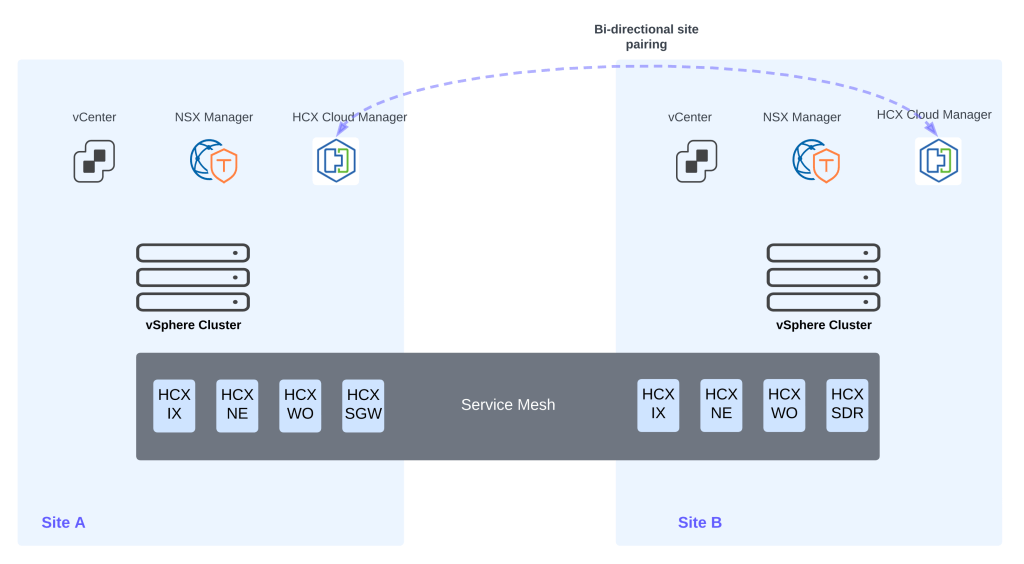
Bidirectional Site Pairing:
In bidirectional site pairing, HCX Cloud systems are site paired with each other, share a common Service Mesh, and can initiate Migration and Network Extension operations from either HCX Cloud system.
Above figure shows bidirectional site pairing between HCX cloud managers.
HCX Cloud to HCX Cloud bidirectional site pairing does not rely on HCX connector.
HCX Data plane components:
As shown in above figures, HCX service mesh consists of appliances such as HCX IX, HCX NE, HCX WO, HCX SGW. Note that these appliances are deployed in a symmetric fashion across the two sites. We will now discuss more about these appliances
HCX interconnect appliance HCX-IX

The Interconnect service (HCX-IX) appliance provides replication and vMotion-based migration capabilities. Which means that this appliance provides capabilities such as workload migration, disaster recovery capabilities. HCX IX appliance establishes IPSec tunnel with peer HCX IX appliance in remote data center. This IPSec tunnel is auto-configured by VMware HCX.
WAN Optimization Appliance HCX WO

HCX WAN Optimization appliance improves utilization of WAN link by using optimization techniques such as de-duplication.
Network Extension Appliance HCX NE

Using HCX Network Extension appliance, networks can be layer 2 extended between sites. This allows workloads being migrated to retain the same IP address and same gateway IP without the need to re-IP. HCX NE appliance establishes IPSec tunnel with peer HCX NE appliance in remote data center. This IPSec tunnel is auto-configured by VMware HCX. At the destination side or target data center, the network backing is always NSX overlay network backed. From the source, you can extend VLAN backed port groups or NSX overlay segments.
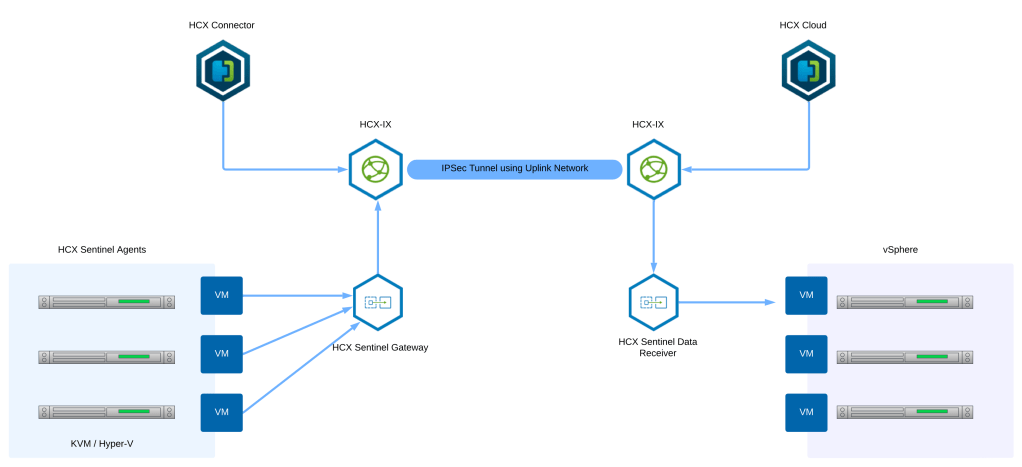
Sentinel Gateway Appliance HCX SGW

VMware HCX has OS Assisted Migration OSAM service using which you can migrate non-vSphere guest virtual machines to vSphere virtual machines. In multi-site mode, HCX deploys the Sentinel Gateway (SGW) appliance at the source vSphere environment for connecting and forwarding guest workloads. The HCX Sentinel Gateway must be deployed in a vSphere environment, and not within KVM or Hyper-V. You must install the HCX Sentinel agent in all the KVM or Hyper-V workloads you wish to migrate.
HCX Sentinel Data Receiver Appliance

Figure above shows how HCX deploys the Sentinel Data Receiver (SDR) appliance at the destination vSphere environment for receiving, managing, and monitoring data replication operations. As shown in the figure above, this appliance works alongside Sentinel Gateway Appliance to migrate non-vSphere guest virtual machines to vSphere virtual machines.
With this, we have covered important VMware HCX use cases and the overall architectural components of VMware HCX.


One thought on “VMware HCX use cases and HCX Architecture”