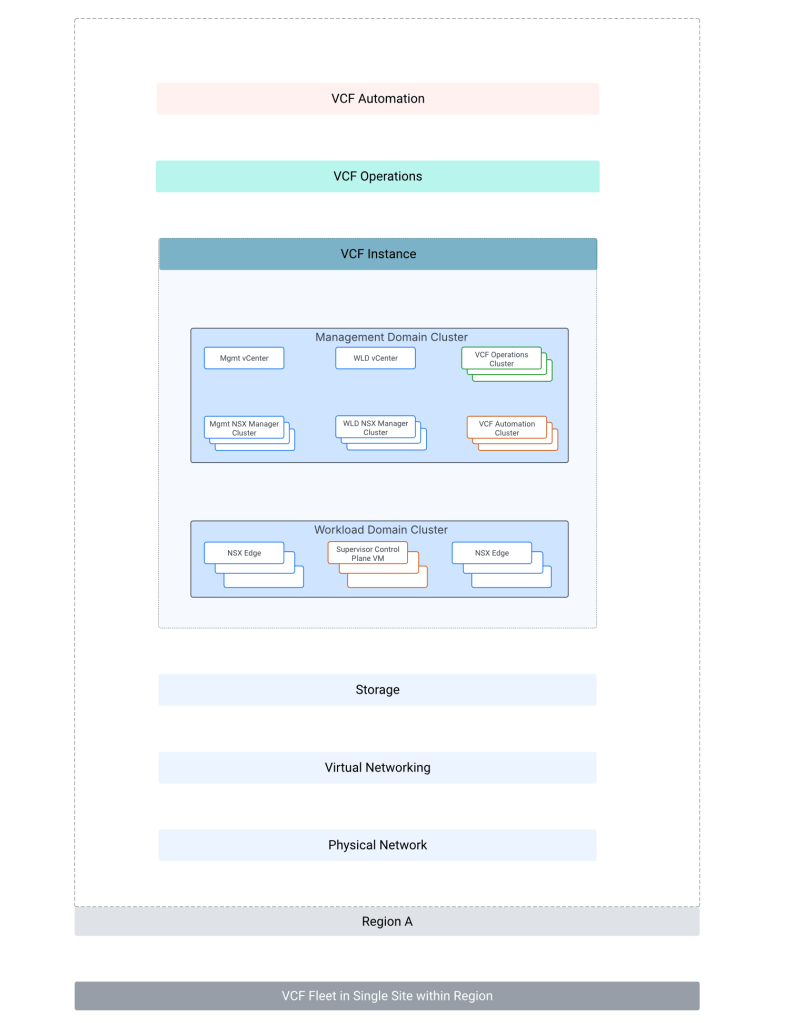
VCF Architectural Components:
Above VCF architecture is for a VCF fleet in a single site within a region.
A VCF fleet consists of:
- VCF Operations
- VCF Automation
- One of more VCF instances (A VCF instance typically has a management domain and multiple workload domains).
- Management domain has management components (vCenter server, NSX manager, VCF Operations, VCF Automation) of VCF deployed.
- Workload domain can contain one or more vSphere clusters for hosting customer workloads.
Overview of VCF Automation
VCF Automation allows provider admins to build secure, multi-tenant clouds by pooling virtual infrastructure resources such as VMware vSphere, vSAN and NSX. VMware vSphere, vSAN and VMware NSX provide compute, storage, networking & security resources for VCF Automation.
VCF Automation capabilities can be utilized in:
- An enterprise to cater to the requirements of multiple internal tenants (HR team, finance team, IT Operations team, Development team, QA team etc. ) or
- VCF Automation multi-tenancy capabilities can be used in a service provider infrastructure where there is a need to provision infrastructure for multiple customers or tenants.
VCF Automation automatically discovers all vCenter and NSX instances registered in VCF Operations of VCF 9.
vSphere Supervisor (which is a collection of one or more clusters on a vCenter instance that provide and manage Kubernetes resources) and NSX edge clusters are also auto-discovered by VCF Automaton. There is no need to explicitly add these components to VCF automation.
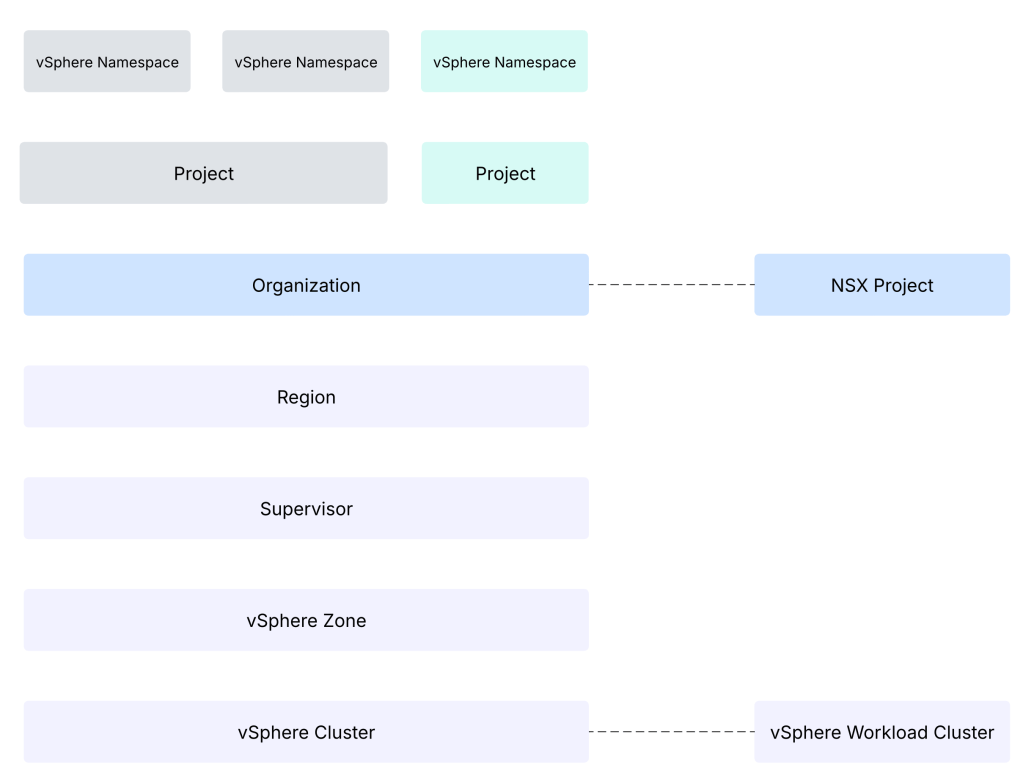
vSphere supervisor is enabled on the vSphere workload cluster which belongs to workload domain of VMware Cloud Foundation 9. VCF Automation Organization workloads run on vSphere supervisor. A vSphere supervisor can only be mapped with one VCF Automation Region.
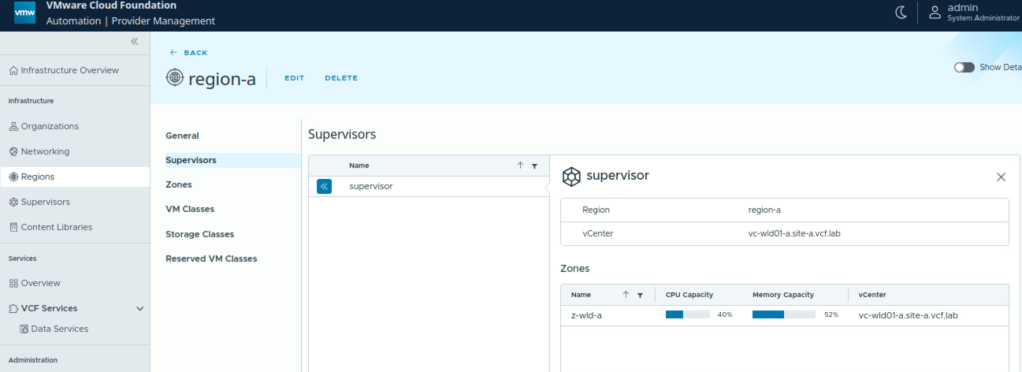
vSphere Zone: A Supervisor can span across multiple zones whereby each vSphere zone maps to a vSphere cluster. In this scenario, the supervisor control plane VMs are distributed across the three vSphere clusters. A vSphere namespace configured on top of such a vSphere supervisor can span three vSphere zones.
VCF Automation related concepts:
Region: A region combines the compute, memory, and networking resources from the underlying infrastructure. For example it can combine vSphere, vSAN and NSX resources into a region. A region can be created by grouping one or more Supervisors from one or more vCenter instances, all supervisors need to be configured under the same NSX Local Manager. You can use multiple regions to meet diverse service level requirements. Multiple regions can be created for different geographies, business units, or performance needs etc.
Resources in a region can be dedicated to a single organization or shared across multiple organizations.
VCF Automation Organization: VCF Automation Provider Management Portal is used to configure VCF Automation Organization. Organization boundary includes resources, users, policies, IaaS services, and catalog entities specific to a VCF Automation Organization. VCF Automation Provider Management portal is used to set quotas and VM and storage classes for an organization. Organization boundary provides isolation from the other VCF Automation organizations. An organization can map to a tenant, a customer, line of business (IT, Development, Quality Assurance teams, etc.).
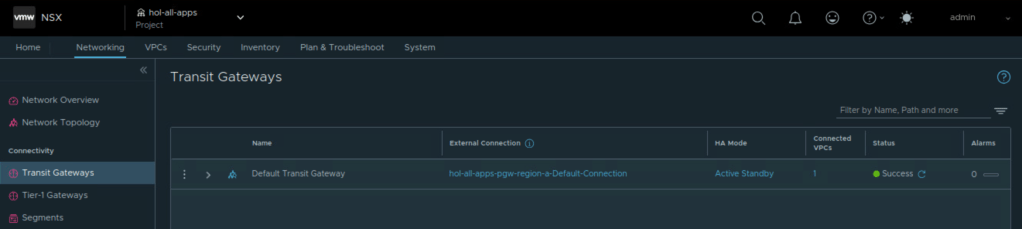
It is important to note that a VCF Automation Organization maps to a NSX project. This means that VCF Automation Organization will eventually have only one NSX transit gateway to communicate with anything external to the organization.
VCF Automation Organization types:
All Apps Organization: Allows organization admins to provision VMs, Kubernetes, networking, volumes, Secret Store, databases, Harbor container registries, external DNS, certificates, and AI workloads.
VM Apps Organization: This is to help existing VMware Aria Automation users transition to VCF Automation 9.0 without any impact to infrastructure, automation, or end-user experience. In VM Apps organizations, the allocation of resources, like cloud accounts, cloud zones, profiles, image mappings and so on, is contained in the organization itself.
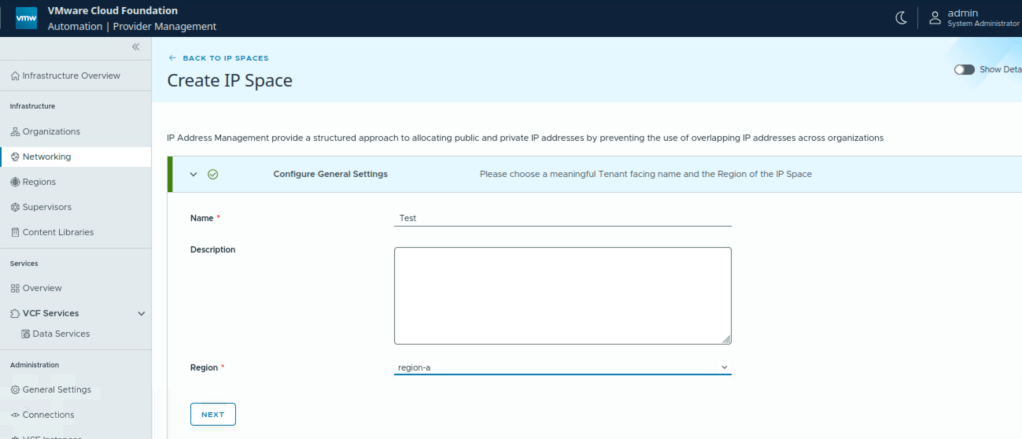
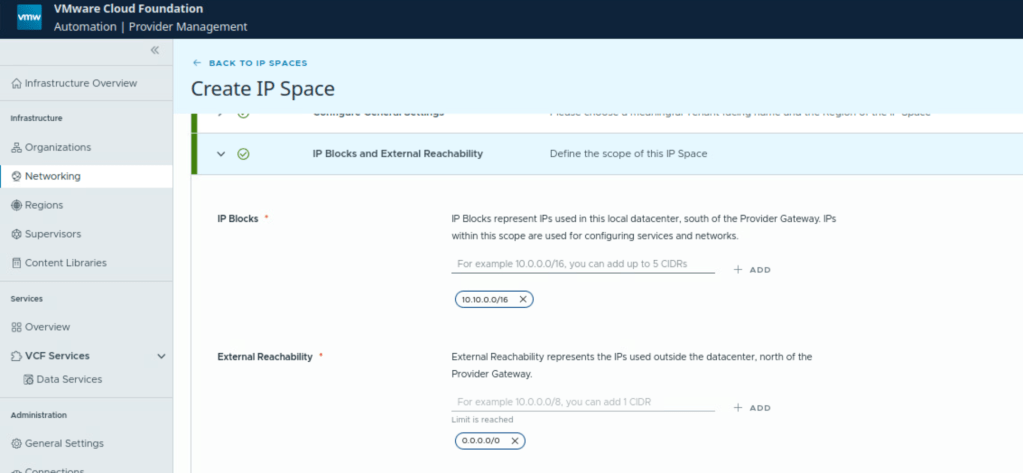
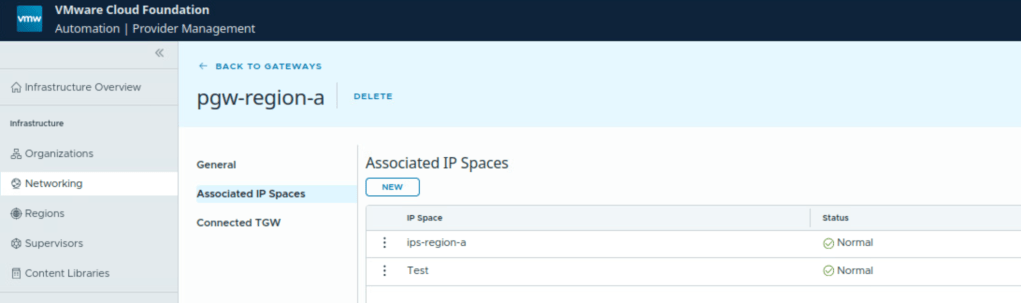
IP Spaces: It provide a structured approach to allocating public IP addresses to different organizations. It consists of a set of CIDR blocks that are used by organization administrators as they configure services. It represents IPs used in this local datacenter, south of the provider gateway, used for configuring services and networks. Provider Administrator can create IP spaces and assign them to provider gateways.
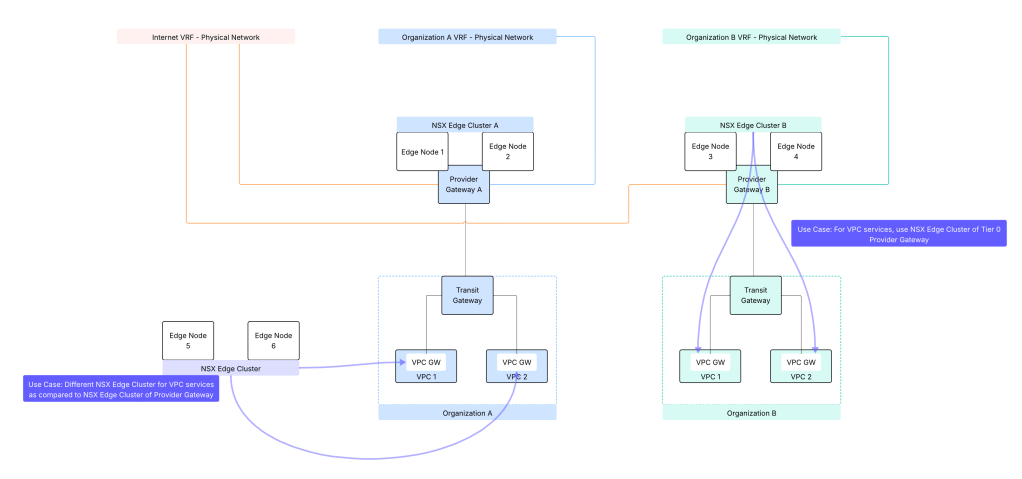
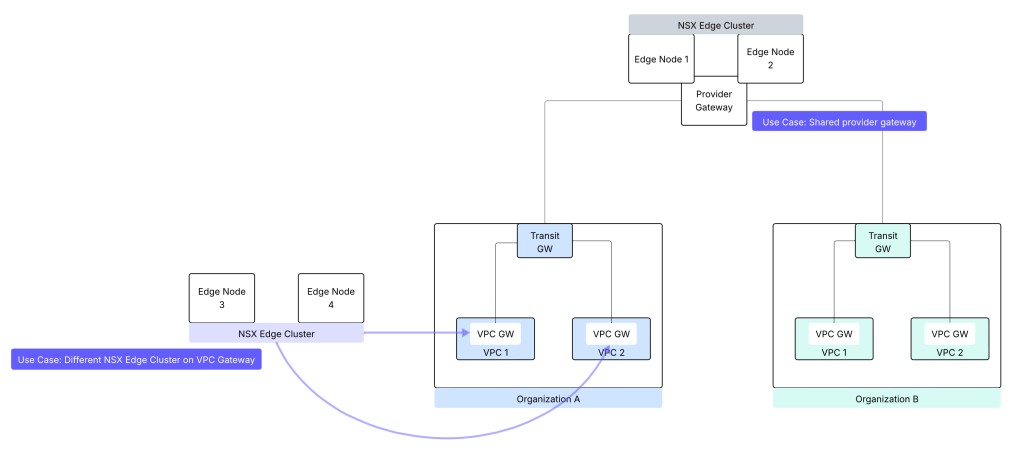
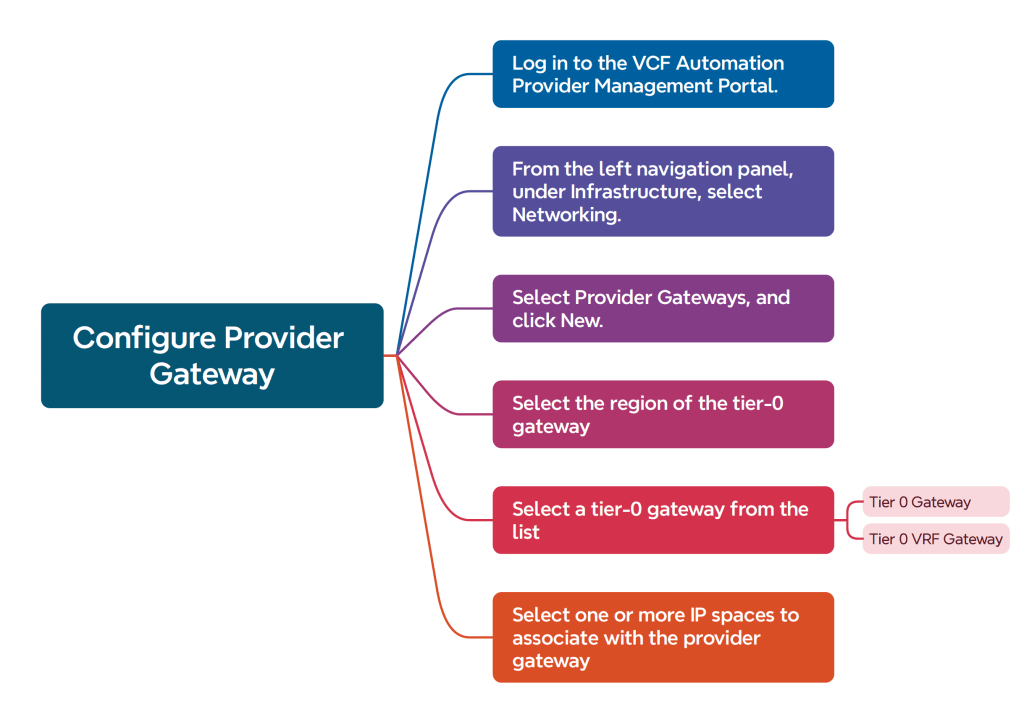
Provider Gateway: A provider admin can configure provider gateway to allow external network connectivity for an organization. A provider gateway in VCF automation will map either to NSX Tier 0 Gateway or to NSX Tier 0 VRF gateway. For VCF Automation use-case, NSX Tier 0 Gateway or NSX Tier 0 VRF gateway is configured in Active/Standby high availability mode.
A provider gateway is associated with IP Spaces, those IP spaces are advertised from the provider gateway.
A provider gateway is mapped to an organization. A provider gateway can optionally be shared across more than one organizations.
Create a region in VCF Automation
Before you configure a region, verify that your vCenter instance has a Supervisor enabled.
This lab has a pre-configured VCF Automation Region.
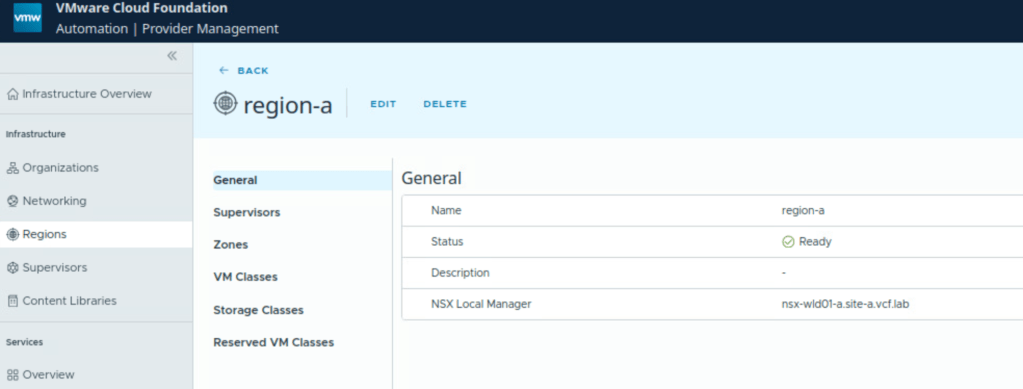
Once a region is configured, you can check:
- NSX Local Manager associated with the region
- vSphere Supervisor and vsphere zone associated with this region
VCF Automation Organizations
VCF Automation Organization maps to a NSX Project. VCF Automation Provider Management Portal is used to create, configure, and manage VCF Automation organizations.
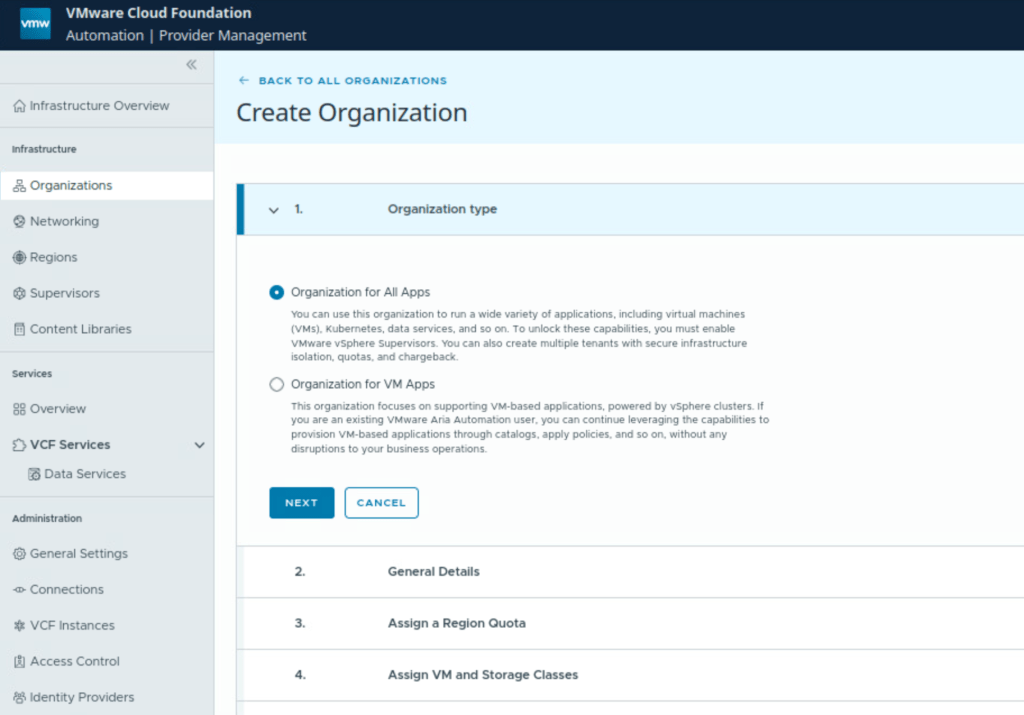
How to create an Organization in VCF Automation
Navigate to Infrastructure – Organizations
Click Create Organization
Give the Organization a name.
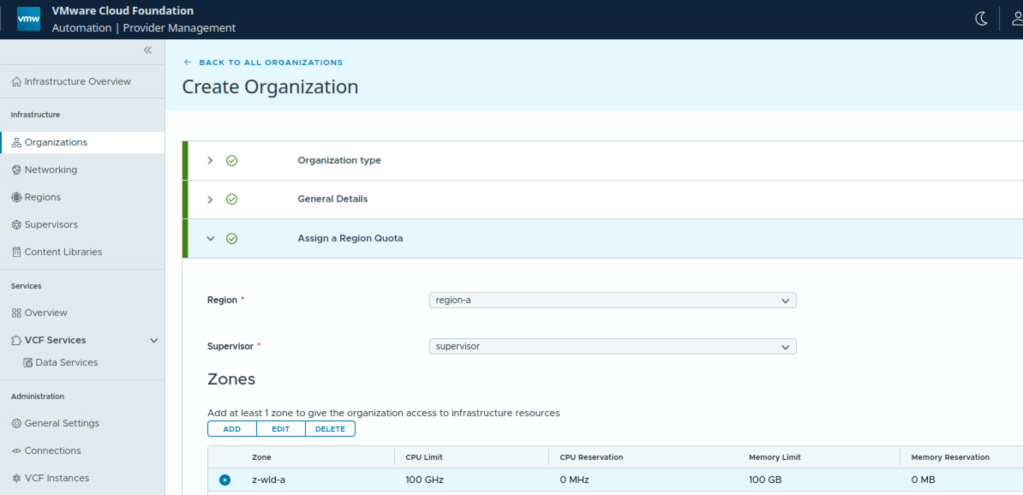
Assign region, supervisor, vSphere zone.
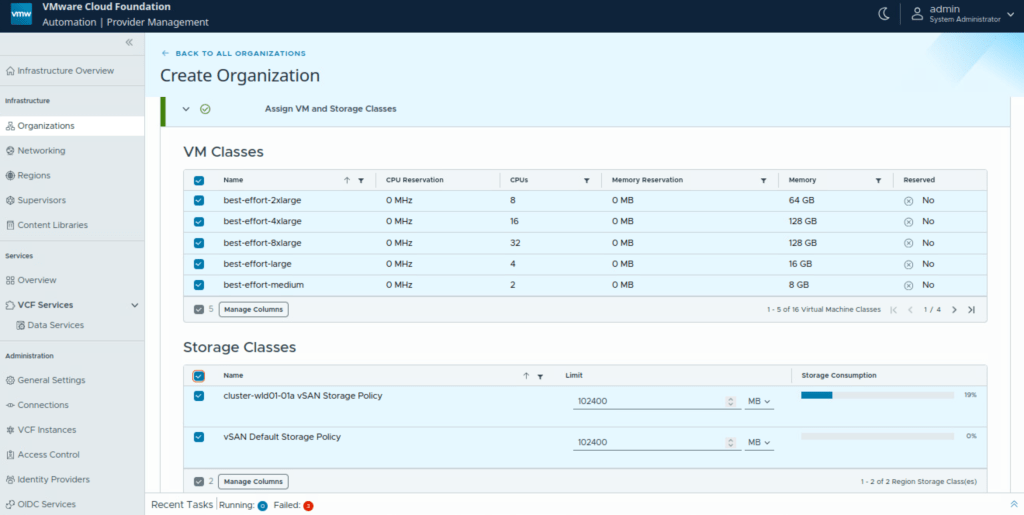
Assign VM classes and storage classes.
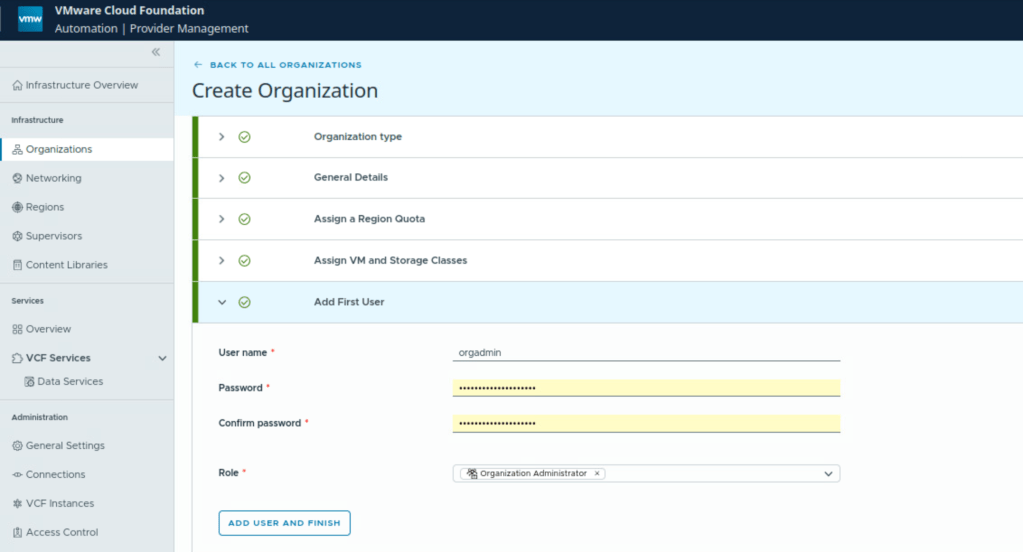
Assign Organization Admin for the VCF Automation Organization.
IP Spaces
IP blocks: These are IP addresses which are used to the south of the provider gateway for configuring services and networks.
External reachability: These are IPs which are to the north of the provider gateway associated with this IP Space.
Configure provider gateway before configuring networking for the VCF Automation Organization
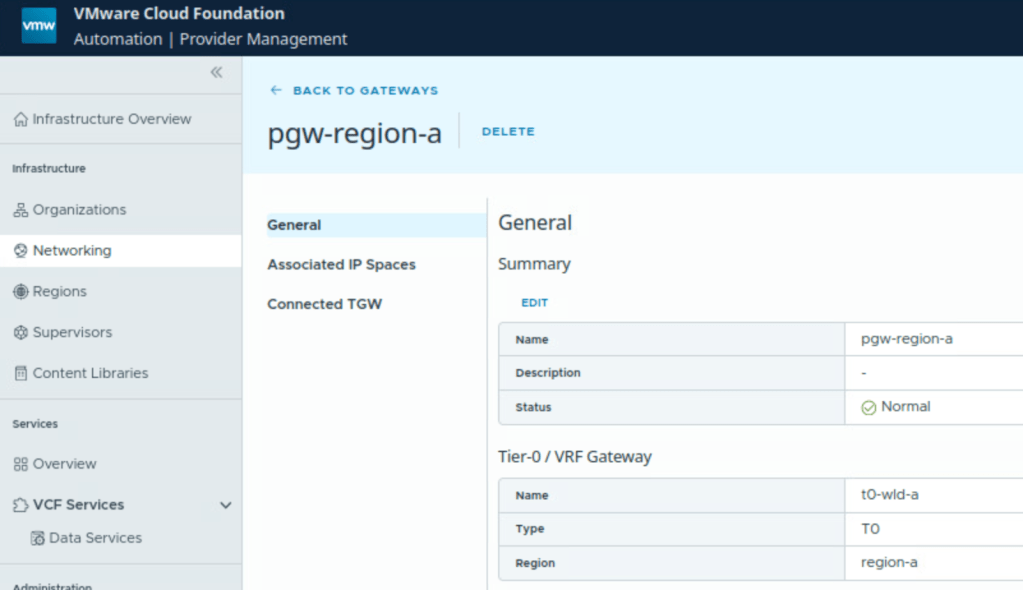
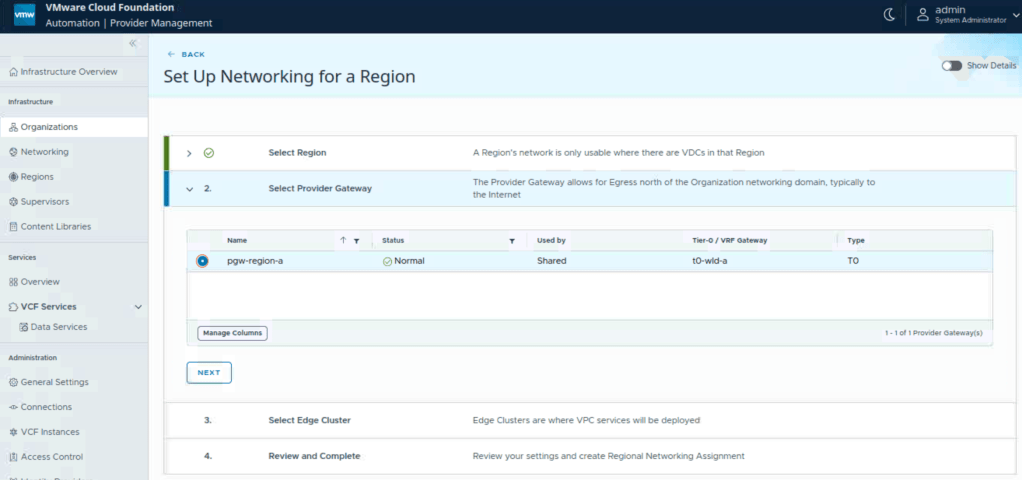
In this case, there is a pre-configured provider gateway, we can verify that:
- Provider gateway is mapped to a Tier 0 Gateway of NSX.
- It is mapped to IP Space
Configure networking for the VCF Automation Organization
Provider management portal is used to configure networking for VCF Automation Organization.
Navigate to Organizations and select the organization for which you wan to set up networking.
Click on Networking
If you do not have a log name for the organization, under General, click Edit, and enter a name.
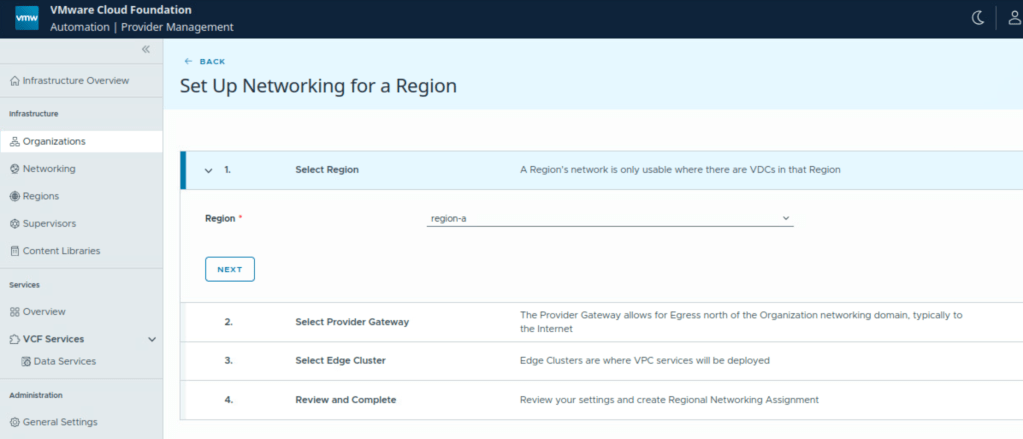
Under regional networking, click on New.
Select pre-configured region
Select provider gateway for this organization.
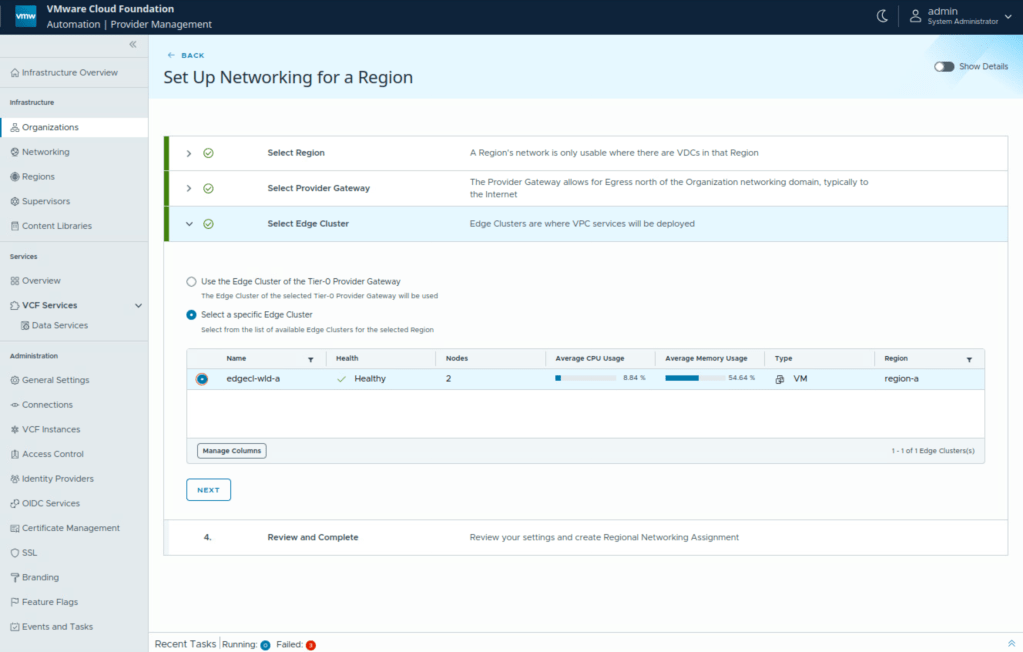
Select NSX edge cluster which will be utilized for NSX VPC services. You have the option to use the same NSX edge cluster as that on the provider gateway or use a different NSX edge cluster as compared to the NSX edge cluster of provider gateway.
Completing this configuration creates an NSX Project, an NSX Transit Gateway, a default VPC, a default VPC connectivity profile, and an outbound SNAT rule which provide connectivity up to the tier-0 gateway.
Validation on NSX side
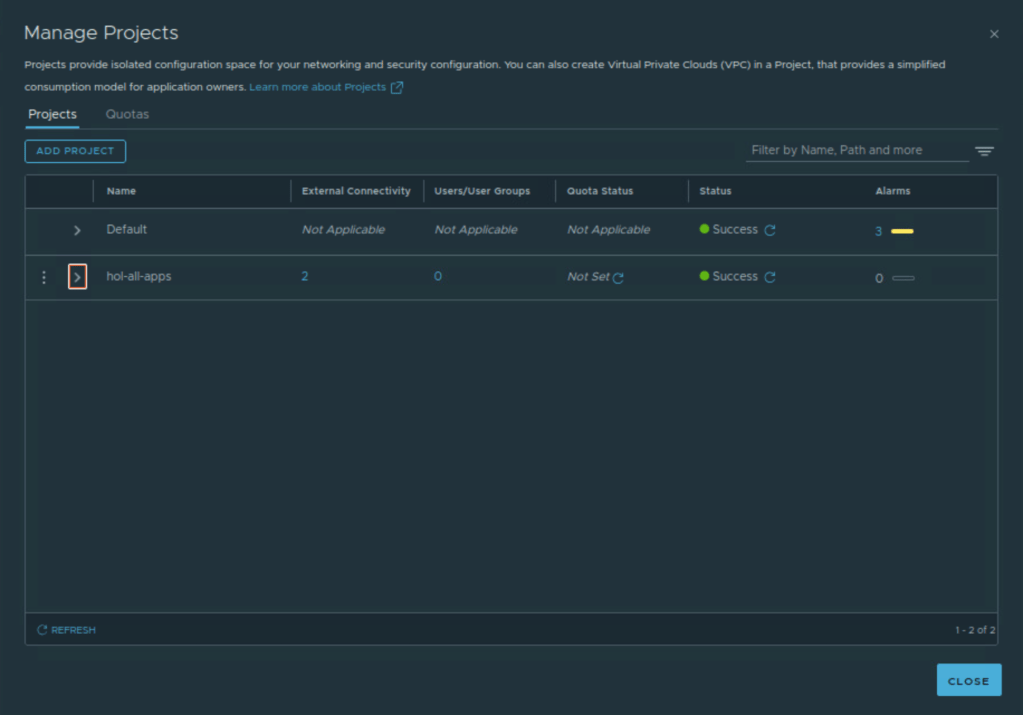
Organization in VCF Automation maps to NSX Project on NSX side. Each VCF Automation organization has one NSX Project per NSX Manager.
On NSX Local Manager side, you will notice corresponding NSX project has been created automatically with the name that you provided for the VCF Automation Organization.